News Releaseï¼ڑPioneer Succeeds in DevelopingHigh Performance 8-VSB Demodulation Algorithm for DTVImproves the performance of indoor reception
Information contained in the news release is current as of the date of announcement.
It is subject to change without prior notice.
Pioneer Corporation
Pioneer Succeeds in Developing
High Performance 8-VSB Demodulation Algorithm for DTV
Improves the performance of indoor reception
Tokyo, Japan, July 5th, 2000 --- Pioneer Corporation ( Head Office: Tokyo Japan / President: Kaneo Ito ) announced that it has succeeded in developing a high performance 8-VSB *1 demodulation algorithm for use in DTV (Terrestrial Digital Television of North America) receivers. This technology has a special adaptive equalization algorithm feature*2 and has the advantage of robustness against multi-path*3.
The performance of indoor reception will be improved a great deal with this new technology.
Background of the Development
In November 1998, terrestrial digital television broadcasting began in the United States. During the development of related DTV receivers, Pioneer has been developing 8-VSB demodulation technology.
It has been reported that 8-VSB systems have difficulty with indoor reception because of the poor performance of indoor antennas affected by the problem of multi-path. This has become one of the major problems with digital TV reception in the U.S., where manyhouseholds use indoor antennas.
Pioneer has paid particular attention to the problem of indoor reception from the beginning and has extensively researched the related reception technology. As a result, the company has at last succeeded in developing a high performance demodulation algorithm that is highly resistant to multi-path.
< Features >
The developed 8-VSB demodulation technology has a special feature in the form of an adaptive equalizer. The brand-new architecture derived from the equalization algorithm demonstrated high performance in eliminating the inter-symbol interference caused by short delay multi-path (*4) and dynamic multi-path (*5). ( See Technical Note )
Pioneer has also developed a trial LSI and evaluated its performance in practical field tests.
The digital modulation scheme specified in the ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee) standard, where three bits of binary data are mapped into eight discrete amplitude levels that will modulate the amplitude of a carrier wave suppressed with a prescribed vestigial sideband shape.
The signal processing method to eliminate the inter-symbol interference of received symbol.
A propagation phenomenon which results in more than one signal reaching the receiver, one by a direct path, the other by a reflected or distorted path.
One signal by a direct path, the other by a short delay reflected or distorted path.
One signal by a direct path, the other by a dynamic varying reflected or distorted path.
< Technical Note >
The following graph shows the expected performance of Pioneer's new equalizer. Here its performance is evaluated in comparison with a conventional Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) that is widely employed in current DTV receivers.
The performance of both equalizers were evaluated in seventeen multi-path-conditions that were sampled in actual field conditions*1. On the graph, the required C/N*2 at TOV*3 is plotted for each multi-path-condition. For example, in multi-path-condition `A`, where the conventional DFE requires 28dB C/N for acceptable reception, our equalizer can work properly even at 20dB C/N. Here, we can easily imagine that a current DTV receiver with a conventional DFE cannot demodulate the signal even though the reception point is near the transmitter.
For all multi-path-conditions, our equalizer shows better performance than the conventional DFE. It should also be mentioned that the advantage of our equalizer is more than 5dB in five multi-path-conditions. As a result, we believe that our new technology can largely extend the service availability of DTV.

Search for Other resources
Search for Keyword
Search by date
-
December 12, 2025Research and developmentPioneer Develops AI Agent for Next-Level in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) with Microsoft Foundry
AI and cloud solutions combine to bring innovative UX and greater safety to a variety of vehicles
-
July 11, 2022Research and developmentHelping to Achieve Carbon Neutrality with Technologies
to Estimate and Predict fuel economy and electricity mileages
of vehicles
-Supporting CO2 emission reductions in the mobility environment
with the proprietary platform â€کPiomatix for Green’-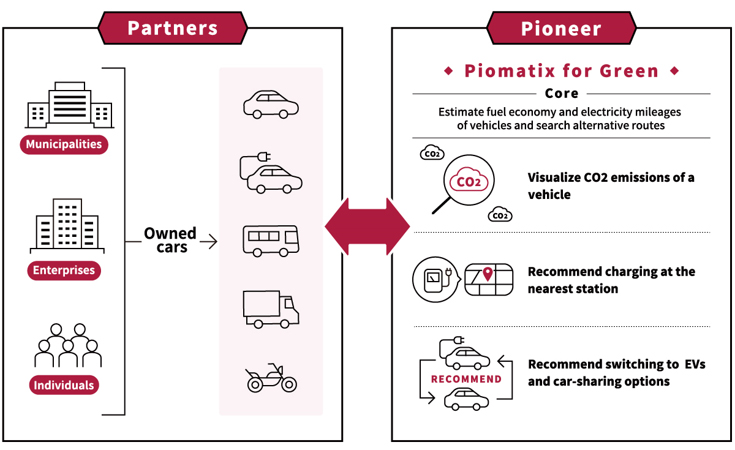
-
November 25, 2020Research and developmentPioneer’s approach for telematics service for high efficient global logistics in ASEAN Selected for JETRO “The Program for Strengthening Overseas Supply Chainsâ€
- Contributing to improving logistics performance with a logistics planning optimization solution utilizing driving video data -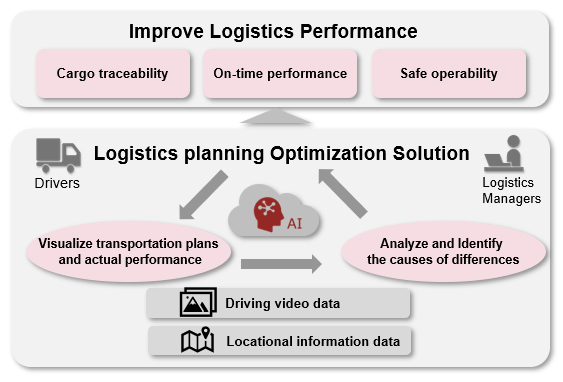
-
October 13, 2020Research and developmentTohoku Pioneer Agrees to Supply OLED Panels to PolyPhotonix for its Sleep Mask Treating Diabetic Retinopathy

-
February 6, 2020Research and developmentParticipated in an autonomous driving demonstration under 5G environment in Malaysia - Expand demonstration area for commercialization of autonomous driving service in ASEAN region - (PDF 281 KB)

-
January 8, 2020Research and developmentPioneer Unveils “Next-Generation 3D-LiDAR Sensor†Capable of Measurement at Long Distance of 500 m, Exhibits Prototype at CES2020 -Lineup of 1550nm wavelength sensor model, catering to diverse markets and customer needs- (PDF 234 KB)

-
January 8, 2020Research and developmentPioneer Exhibits “3D Data Collection LiDAR kit†Retrofittable on Vehicles at CES 2020 - Detect the environment around the vehicles with high resolution, providing data for map maintenance and other applications - (PDF 273 KB)

-
December 19, 2019Research and developmentPioneer Develops Mass-Production Model of 3D-LiDAR Sensor with Improved Measurement Distance and a Much Compact Size -Models supporting level-three and above autonomous vehicles will be mass-produced in autumn 2020- (PDF 516 KB)

-
May 30, 2019Research and developmentPioneer and Arm Treasure Data Reached an Agreement for Co-Development of Data Analysis/Behavior and Accident Risk Prediction Models Based on AI Technology in Mobility (PDF 105 KB)

-
April 17, 2019Research and developmentPioneer and Canon agree to co-develop 3D-LiDAR sensor, drive the development of compact, high-performance 3D-LiDAR sensors (PDF 88 KB)

